Three daily habits could be prematurely aging your skin by destroying the essential protein that keeps it firm and youthful.
At a Glance
- Smoking introduces toxins that directly damage collagen, leading to premature wrinkles and sagging skin
- Unprotected sun exposure breaks down collagen fibers through UV radiation, accelerating skin aging
- High sugar consumption causes glycation, which stiffens collagen and reduces skin elasticity
- Protecting collagen through lifestyle changes can help maintain skin health even as you age
Understanding Collagen’s Crucial Role in Skin Health
Collagen makes up approximately 70% of the protein in your skin and serves as the structural foundation that keeps it firm, resilient, and youthful. This essential protein is found throughout the body in tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, and bones, providing strength and structure. As we age, our natural collagen production begins to decline, typically starting in our mid-20s and accelerating in our 40s and beyond. This natural decrease contributes to the formation of wrinkles, loss of volume, and decreased skin elasticity that are hallmarks of aging skin.
While some collagen loss is inevitable with aging, certain lifestyle factors can dramatically accelerate this process. By understanding these collagen-destroying habits and making simple adjustments, you can significantly slow down unnecessary collagen degradation and maintain healthier skin as you age. The three most destructive habits—smoking, unprotected sun exposure, and high sugar consumption—deserve particular attention, as eliminating these factors can preserve your skin’s natural collagen reserves.
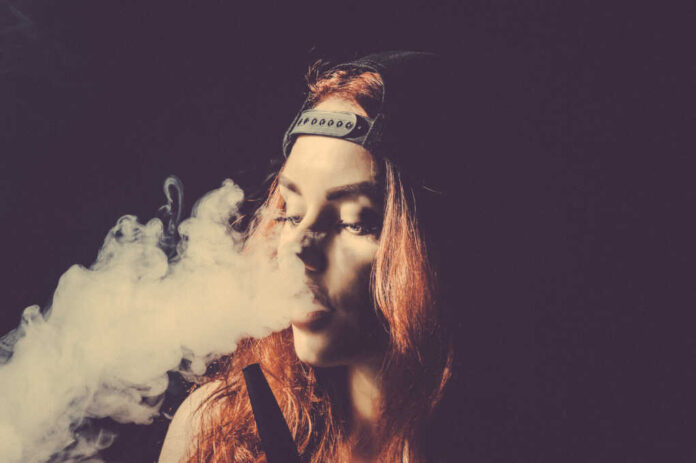
The Destructive Impact of Smoking on Skin
Smoking is perhaps one of the most damaging habits for collagen health. Each cigarette introduces over 4,000 chemicals into your body, many of which directly attack collagen fibers. The toxins in tobacco smoke trigger an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes that break down collagen and elastin. Additionally, smoking constricts blood vessels, reducing oxygen and nutrient flow to the skin, which further impairs collagen production and repair mechanisms.
The visual effects of smoking on skin become apparent surprisingly quickly. Smokers typically develop more pronounced wrinkles around the mouth and eyes, a grayish skin tone, and accelerated sagging of facial features. Studies have shown that heavy smokers can appear 10-20 years older than their non-smoking counterparts of the same age. Quitting smoking allows the body to begin repairing some of this damage, with improved circulation and decreased inflammation supporting better collagen production over time.
— Tom Adelstein (@AdelsteinTom) April 16, 2025
How Sun Exposure Breaks Down Collagen
Unprotected sun exposure is responsible for an estimated 80-90% of visible skin aging, with its destructive effects on collagen being a primary factor. UV radiation penetrates the skin and creates free radicals that damage collagen fibers. This photodamage triggers a abnormal buildup of elastin and the activation of enzymes that break down collagen. The result is a process called solar elastosis, where the skin develops a leathery, wrinkled appearance and loses its ability to snap back into place.
Daily sun protection is essential for preserving collagen, even on cloudy days and during winter months. A broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher should be applied every morning and reapplied throughout the day when outdoors. Physical barriers like wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing provide additional defense. Remember that UV damage is cumulative over your lifetime, so it’s never too late to start protecting your skin and preserving the collagen you have left.
The Sweet Threat: How Sugar Damages Collagen
The third major enemy of healthy collagen is excessive sugar consumption. When we consume sugar and simple carbohydrates, they attach to proteins in the bloodstream through a process called glycation, forming advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These AGEs bind to collagen and elastin fibers, causing them to become stiff and malformed. The result is skin that loses its suppleness and develops premature wrinkles. This process accelerates significantly when blood sugar levels are consistently elevated.
Reducing sugar intake can have remarkable effects on skin health and collagen preservation. Focus on complex carbohydrates, which break down more slowly and cause less glycation. Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants, which can help protect collagen from glycation damage. Berries, leafy greens, nuts, and green tea are particularly beneficial. Staying well-hydrated also supports optimal cellular function and helps maintain the moisture content in the skin, allowing collagen to function properly.
Here’s another one for you.
Blueprint went viral and the second most frequent comment was “I want to do your protocol, but it’s way too complicated, make it easy.”
#1 was “I hate you and want you to die” in various forms.
Anyways, my team and I did it. Blueprint is the… pic.twitter.com/muouyg7LEn
— Bryan Johnson (@bryan_johnson) January 6, 2025
Supporting Collagen Through Positive Habits
While avoiding collagen-damaging behaviors is crucial, you can also actively support collagen production through positive habits. Consuming collagen-rich foods like bone broth, fatty fish, and chicken skin provides your body with the building blocks needed for collagen synthesis. Vitamin C is essential for collagen production, so incorporate citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries into your diet. Adequate sleep allows your body to repair and regenerate collagen, while regular exercise increases blood flow, delivering nutrients to skin cells.
Topical ingredients like retinoids can also stimulate collagen production in the skin. “Retinoids basically tell our skin to act the way it did when we were younger,” notes Tracy Thaden. Starting with a low concentration and gradually increasing usage can help minimize irritation while maximizing benefits. For those seeking additional support, collagen supplements in the form of hydrolyzed collagen peptides have shown promising results in some studies, though they work best as part of a comprehensive approach to skin health.