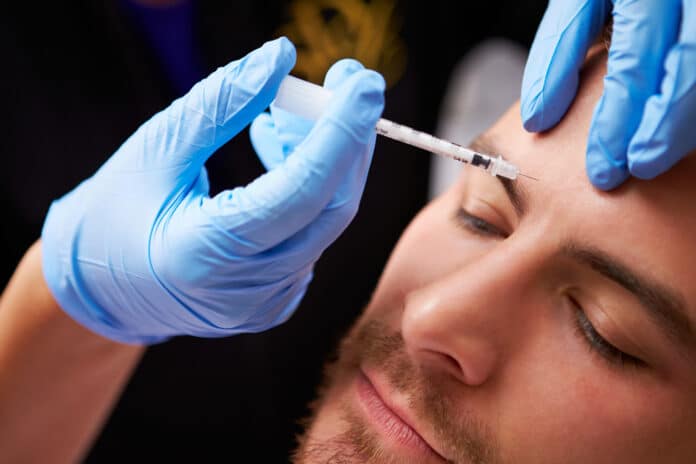
Botox is an injectable drug made from botulinum toxin type A, which is created by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. When injected, Botox stops signals from your nerves to your muscles. This prevents the targeted muscles from contracting, which can ease specific muscular issues and improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Interesting, right? But are there any downsides to this practice? This article examines botox’s long-term side effects, its safety, and its common uses.
What Are Botox’s Long-Term Side Effects
Since the effects of Botox injections are temporary, most individuals get repeated injections over time. However, research on long-term effectiveness and safety is limited.
According to a 2015 study assessing the effects in participants who received Botox injections every 6 months to treat bladder conditions, the risk of adverse effects didn’t increase over time. Individuals who received repeated injections also had better long-term treatment success.
However, the results of a 2015 research review suggest that adverse effects may appear after the 10th or 11th injection. For instance, researchers in a 2005 study observed 45 participants who regularly received Botox injections over 12 years. During this time, 20 cases of adverse side effects were recorded, including:
● Nausea
● Difficulty swallowing
● Vomiting
● Blurred Vision
● Drooping eyelid
● Heart palpitations
However, more research is needed to understand the long-term side effects of Botox.
Is Botox Safe?
Although botulinum toxin is life-threatening, the small doses used in the application of Botox are considered safe. Between 1989 and 2003, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) received 1031 adverse effects reports linked to the use of Botox. Among those cases, only 36 were considered severe and 995 non-serious.
Additionally, 6 of the severe cases may have been caused by an underlying condition and not the drug itself. Considering this, some researchers speculate that cosmetic applications could have less risk than therapeutic Botox injections due to much smaller doses.
How is Botox Used?
Botox is commonly known for its capability to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. For instance, Botox can relax the muscles that cause:
● Frown lines between the eyebrows
● Forehead creases
Botox is also used for treating underlying muscular conditions such as:
● Chronic migraine
● Eye twitching
● Overactive bladder
Conclusion
If you’re considering Botox treatments, working with a licensed and experienced healthcare professional is crucial. Additionally, side effects might also be possible due to the procedure. As such, talk with your doctor about what to expect during the injection process and the subsequent recovery period.