Type 2 diabetes, once considered a lifelong condition, can now be reversed through targeted diet and exercise interventions, allowing many patients to achieve remission without medication.
At a Glance
- Type 2 diabetes remission is now recognized as possible by major health organizations, challenging the traditional view of the disease as irreversible
- Weight loss of approximately 15kg is necessary for most people to achieve diabetes remission, with early intervention offering the best chance of success
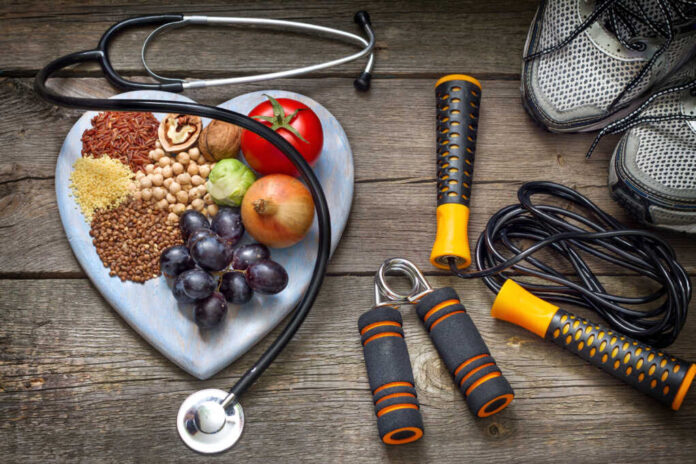
- Plant-based diets, regular exercise, and sustainable lifestyle changes have shown similar effectiveness to bariatric surgery for diabetes remission without side effects
- Diabetes is considered in remission when blood glucose levels remain below diagnostic thresholds for at least three months without medication
- The Personal Fat Threshold concept explains that diabetes occurs when fat exceeds an individual’s tolerance, not necessarily at obesity levels
The Shifting Paradigm of Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Type 2 diabetes affects over 830 million people worldwide, with 91% of all diabetes cases falling into this category. In the United States alone, approximately 10.5% of adults live with the condition, and alarmingly, 21% remain undiagnosed. For decades, medical professionals viewed this metabolic disorder as a progressive, irreversible condition requiring lifelong medication management. However, this perspective has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years as mounting evidence demonstrates that type 2 diabetes can actually be reversed through appropriate lifestyle interventions.
The World Health Organization, American Diabetes Association, and other leading health authorities now acknowledge diabetes remission as a viable treatment goal. Diabetes remission is defined as maintaining blood glucose levels below diagnostic thresholds for at least three months without medication. This significant shift in understanding gives hope to millions while emphasizing the critical role of diet, exercise, and weight management in treating this condition.
Credit where it’s due; they deprescribed a ton of medications
I’d like to know when that deprescription occurred though. Did they keep glp1s on until the very last moment right before the end of the study? Or did they stop them in the first month and subjects had continued… https://t.co/awyscekzfX pic.twitter.com/jgmgU0yOp6
— Matt Calkins MD MHP (@MattCalkinsMD) May 16, 2025
The Science Behind Diabetes Reversal
At the core of type 2 diabetes reversal is the Taylor Twin Cycle Theory, which proposes that the condition results from excess fat accumulation in the liver and pancreas. According to Professor Roy Taylor’s research, this excess fat impairs insulin production and action, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. The theory suggests that reducing this fat through caloric restriction and weight loss can restore normal metabolic function in many patients, essentially reversing the disease process.
A groundbreaking concept called the Personal Fat Threshold helps explain why diabetes doesn’t affect all people with obesity. This theory proposes that each individual has a unique threshold for fat tolerance; exceeding this personal limit triggers metabolic dysfunction, regardless of whether someone meets clinical obesity criteria. This explains why some people develop diabetes at lower body weights while others with higher body weights remain metabolically healthy. The focus shifts from BMI numbers to individual metabolic response to fat accumulation.
Effective Approaches to Diabetes Remission
Research consistently shows that significant weight loss is the primary driver of diabetes remission. The landmark Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT) demonstrated that losing approximately 15kg led to remission in a substantial percentage of participants, particularly those diagnosed within the past six years. This weight loss reduces the harmful fat deposits in vital organs, restoring their ability to function normally. Programs like the one at Joslin Diabetes Center report impressive results, with 80% of participants achieving diabetes remission within two years.
Diet plays a central role in achieving this necessary weight loss. Expert consensus increasingly supports plant-based eating patterns high in fiber and low in refined carbohydrates and processed foods. These diets help regulate blood sugar, reduce inflammation, and promote weight loss without severe calorie restriction. Intermittent fasting regimens have also shown promise, though medical supervision is essential. Combined with regular physical activity, which improves insulin sensitivity independent of weight loss, these dietary approaches offer a powerful path to diabetes remission.
Remission of type 2 diabetes in 87% (!!!) of patients
with diet + exercise on top of standard medical treatment !!!!!diet: 25% protein, 50% carb, 25% fat ~500kcal under estimated energy requirement
cardio 150–200min per week + 20min resistance training 2-3x/wk https://t.co/2QsGzX57SQ
— Gil Carvalho MD PhD🌈 (@NutritionMadeS3) May 15, 2025
Sustainable Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Success
While bariatric surgery has been shown to reverse diabetes in many cases, lifestyle medicine offers comparable benefits without surgical risks. A comprehensive approach including diet modification, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep can be as effective as surgery for achieving diabetes remission. The key difference is that lifestyle interventions address the root causes of metabolic dysfunction rather than altering digestive anatomy. These approaches also provide additional health benefits beyond glucose control, including improved cardiovascular health and reduced inflammation.
It’s important to note that while diabetes can be reversed, it is not considered “cured.” Patients who achieve remission must maintain their healthy lifestyle changes to prevent relapse. Early intervention significantly increases the chances of successful remission, highlighting the importance of regular screening and prompt treatment. For those at risk of developing diabetes, prevention through these same lifestyle modifications remains the optimal approach. With proper support and commitment to sustainable changes, many individuals with type 2 diabetes can achieve remission and enjoy improved health and quality of life.