Amid persistent vitamin D deficiency, millions of Americans face increased risks of depression, a concern that calls for urgent public health action.
Story Highlights
- Approximately 29% of U.S. adults are vitamin D deficient.
- Deficiency is linked to mood disturbances and depression.
- Significant demographic disparities exist, with non-Hispanic Black Americans and women at higher risk.
- Public health experts call for expanded food fortification and supplementation.
High Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency in the U.S.
Recent studies reveal that nearly 29% of U.S. adults are vitamin D deficient, a condition with wide-ranging health implications. The deficiency is more prevalent among women and young adults, highlighting significant demographic disparities. Urbanization and lifestyle changes, leading to reduced sun exposure, are major contributing factors, compounded by limited dietary intake and food fortification.
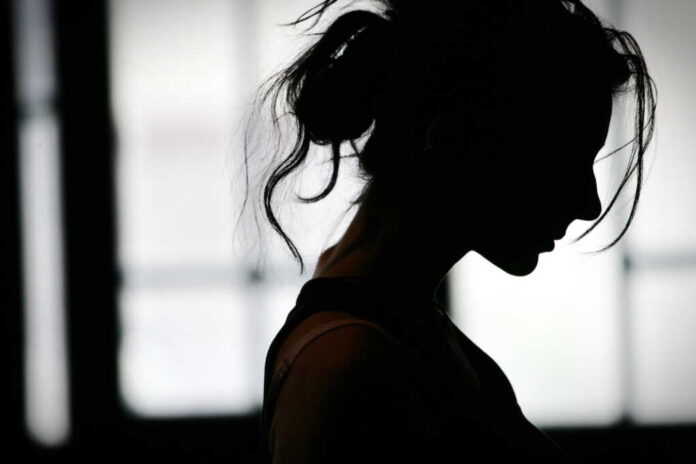
Ongoing discussions emphasize the need for public health initiatives to address this widespread deficiency. Vitamin D, crucial for bone and immune health, is also being recognized for its role in mental health. Deficiency can result in bone pain, muscle weakness, and fatigue, alongside mood-related consequences such as depression, underscoring its public health significance.
Vitamin D is not just a vitamin.
It controls over 2,000 genes, obesity, and every major system in your body.
Yet 1 billion people are deficient, which skyrockets the risk of dying from ALL causes.
Here’s what you need to know (& how to fix it): pic.twitter.com/4VV9odJs9u
— Human Upgrade (@HumanUpgrade_) June 6, 2025
Link Between Deficiency and Mental Health
Emerging research highlights the psychological impacts of vitamin D deficiency, linking it to mood disturbances and depression. Experts argue that vitamin D’s role extends beyond physical health, affecting neurotransmitter functions and mood regulation. This revelation prompts calls for increased awareness and preventive measures, particularly targeting at-risk groups.
Healthcare providers are urged to consider vitamin D status in patients presenting with depressive symptoms, with some experts advocating for routine screening in high-risk populations. This approach, coupled with public education and targeted supplementation, is seen as essential in mitigating the deficiency’s impact on mental health.
Watch: Vitamin D Deficiency: 80% Dementia Risk?! The Shocking Truth #shorts – YouTube
Necessary Public Health Interventions
Addressing vitamin D deficiency requires a multi-faceted public health strategy. Government agencies and healthcare providers play critical roles in implementing these measures, with the potential to significantly reduce the burden of deficiency-related health issues.
Efforts to combat vitamin D deficiency can also stimulate policy debates about optimal serum levels and supplementation guidelines. While some caution against over-supplementation, the consensus remains that proactive interventions are crucial for improving public health outcomes, particularly in reducing the risk of depression and other mood disorders.
Sources:
Vitamin D Deficiency in U.S. Adults: Prevalence, Predictors, and Mood-Related Consequences
CDC Report on Vitamin D Deficiency in U.S.
The Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on Mental Health
Springer Article on Vitamin D Deficiency Trends
JAMA Study on Vitamin D Levels and Health Outcomes