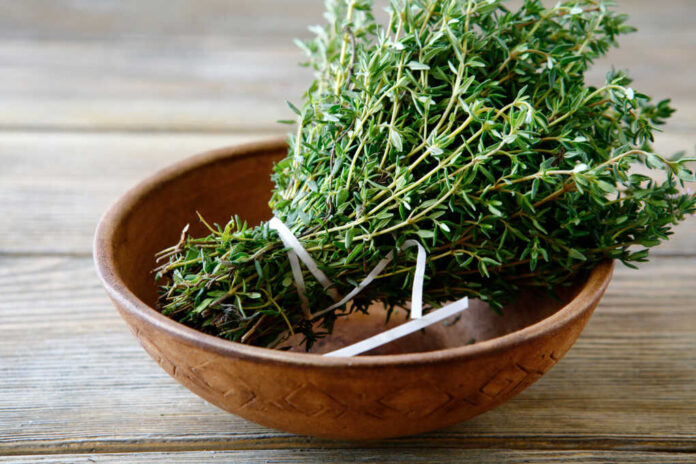
Imagine a future where the humble herb thyme becomes a cornerstone of precision medicine.
Story Snapshot
- Scientists use microfluidics to encapsulate thyme extract for precise nanodose delivery.
- Research published by Tomsk Polytechnic University and Surgut State University.
- Thyme’s bioactive compounds offer potential applications in precision medicine.
- Study bridges traditional herbal remedies with modern pharmaceutical approaches.
Revolutionizing Herbal Remedies
Researchers at Tomsk Polytechnic University and Surgut State University in Russia have taken a bold step by applying microfluidics technology to encapsulate thyme extract into stable microcapsules. This innovative method enables precise nanodose delivery of thyme’s active compounds—thymol, carvacrol, and rosmarinic acid—while mitigating issues like evaporation and irritation. This advancement marks a significant shift from traditional uses of thyme, historically employed for its expectorant, anti-inflammatory, and antiseptic properties.
Traditional medicine has long revered thyme for its therapeutic qualities. However, the challenge has always been the volatility and inconsistent dosing of its compounds. The Russian research team’s method addresses these issues by ensuring consistent nanodoses, a leap forward that could integrate herbal remedies into the realm of precision medicine. This encapsulation technique stands out for its semi-self-organizing nature, offering a scalable solution that extends beyond thyme to other plant extracts.
Scientific Breakthroughs and Potential
The research, published on January 17, 2026, in *Physics of Fluids* by AIP Publishing, has attracted significant attention. It highlights a novel approach that leverages microfluidics to trap thyme’s potent compounds in gelatin-sodium alginate-oil droplets. This technique is designed to be adaptable, with the ability to adjust oil flow rates and integrate with AI and machine vision systems, potentially revolutionizing the way plant-based medicines are delivered.
Maxim Piskunov, the lead researcher, emphasizes the system’s self-regulating capabilities, which are invaluable for drug delivery. The study’s findings could influence both the pharmaceutical and food industries by providing a framework for the incorporation of natural extracts into precision dosing platforms, promising safer and more effective treatments.
How scientists are turning thyme into precision medicine https://t.co/UK4iaIH8Rd
— Un1v3rs0 Z3r0 (@Un1v3rs0Z3r0) January 17, 2026
Industry Implications and Future Prospects
The implications of this research are far-reaching. In the short term, it provides a reliable method for delivering thyme’s bioactive compounds in a stable form, reducing waste and minimizing irritation. Long term, if clinically validated, this could pave the way for integrating herbal remedies into precision medicine, offering patients more personalized and effective treatment options.
Pharmaceutical companies and food industries stand to benefit significantly from this research. The potential for low-cost, scalable microfluidics technology aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and natural therapeutic solutions. For consumers and patients, this means access to medications that harness the power of nature with the precision of modern science.
Meet My Healthy Doc – instant answers, anytime, anywhere.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising outlook, the journey from laboratory to clinical application is fraught with challenges. While the encapsulation method is a proof of concept, further research is necessary to develop suitable packaging for medical use. Clinical trials will be crucial in confirming the efficacy and safety of these nanodose delivery systems, and researchers are currently testing higher concentration extracts to enhance bioactive compound potency.
Experts caution that while the method shows no significant limitations, the path to commercialization will require careful consideration. The emphasis remains on achieving consistent results in in vivo and clinical trials to ensure that these promising developments can be translated into real-world applications. Nevertheless, the potential to revolutionize the delivery of plant bioactives, such as antibacterials and anticancers, is a compelling prospect for the future of medicine.
Your instant doctor companion – online 24 hours a day.
Sources:
Sada News
ScienceDaily
PMC Article
SciTechDaily