According to skincancer.org, melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes and is more dangerous than more common skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma because it rapidly can spread to other organs.
To better understand melanoma, it’s important to know more about melanocytes and the role it plays in our bodies. Melanocytes are upper-layer skin cells responsible for producing a pigment known as melanin. The body produces melanin when exposed to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays, as a way to protect the skin. However, when this production triggers mutations in the melanocytes, cells can begin to grow uncontrollably and thus, lead to melanoma. It’s important to note that UV rays from tanning beds can also cause this same damage.
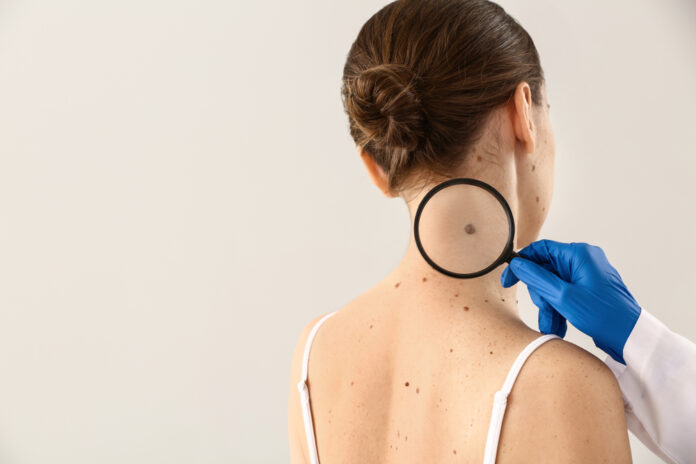
What most people may not know is that melanoma is often present on normal-looking skin versus in just moles, so it can often go undetected. This is one of the major risk factors, being hard to detect and having quick, spreading growth. Although death can happen from melanoma, this form of cancer can be curable especially when detected early. Another dangerous risk is that it can spread to other parts of the body, making it hard to treat and more deadly.
Prevention is key for skin cancer, with reducing exposure to UV rays being the most beneficial. Completely avoiding the sun’s UV rays is not likely or realistic; however, tanning beds should be avoided altogether. Here are the best practices for sun exposure for the prevention of melanoma:
- avoid exposure at the sun’s peak time, between 10:00 am and 4:00 pm
- wear UV protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses
- wear sunscreen with an SPF factor of at least 30 and ensure your product protects against UVA and UVB rays
- reapply sunscreen often
- get regular checkups
Another way to help prevent melanoma is to understand the risk factors associated with it.
- age: melanoma can affect any age, although it is the most common type of cancer amongst young adults. Don’t let your young age make you feel invincible
- family history: those with a close relative that’s been diagnosed with melanoma, are at risk of developing it 2 to 3 times higher than the average
- fair skin: those will fair skin need to be extra cautious, as do those with freckles
- moles: those with many moles, especially unusual ones have a higher risk
- sun exposure: those who have more exposure, especially those with jobs in the sun need to take extra precaution
With knowledge and prevention, melanoma can be detected and easily cured.