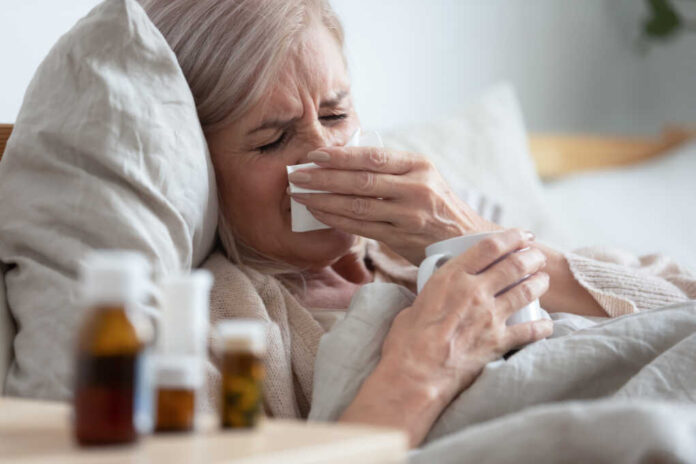
The FDA has issued a new warning about severe itching risks that can occur when patients abruptly stop taking common allergy medications like Zyrtec and Xyzal, affecting long-term users who never experienced itching before.
At a Glance
- The FDA mandated warnings about severe itching (pruritus) risks when stopping cetirizine (Zyrtec) or levocetirizine (Xyzal) after long-term use
- 209 cases of severe post-discontinuation itching were identified between 2017-2023, with 197 cases in the US
- Symptoms typically begin within days of stopping medication and can be serious enough to require medical intervention
- Restarting the medication resolved symptoms in 90% of cases, while tapering after restarting helped others
Understanding the FDA Warning
The US Food and Drug Administration recently mandated a new warning for both prescription and over-the-counter versions of cetirizine (Zyrtec) and levocetirizine (Xyzal). These popular antihistamines, commonly used to treat allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria, have been linked to an unexpected withdrawal effect – severe itching that occurs when patients stop taking them after extended use.
The FDA’s investigation identified 209 global cases of post-discontinuation pruritus between April 2017 and July 2023, with 197 of these cases occurring in the United States. What makes this reaction particularly concerning is that it affects patients who used these medications daily for months or years without having experienced itching symptoms prior to starting the medication.
FDA warns of possible severe itching after stopping long-term use of cetirizine/levocetirizine allergy meds. Warnings added to prescription & OTC drugs. Affects some people after months/years of daily use.
More info: https://t.co/ovlX1431oZ pic.twitter.com/t2bOgBhhUV
— U.S. FDA (@US_FDA) May 19, 2025
Who is at Risk?
The risk appears specifically linked to long-term users who abruptly discontinue these medications. While the exact mechanism behind this withdrawal reaction remains unknown, the FDA has determined there is likely a causal relationship between stopping these antihistamines and the subsequent development of severe itching. The itching typically begins within days of discontinuation and can significantly impact quality of life.
In some documented cases, the itching was severe enough to cause significant distress, with a small number of cases leading to disability, hospitalization, and even thoughts of suicide or self-harm. Although such severe reactions are rare, they highlight the importance of the FDA’s decision to require warning labels on these medications.
Managing Discontinuation
For patients who experience this withdrawal effect, restarting the medication appears to be the most effective solution. According to FDA data, symptoms resolved in approximately 90% of patients who resumed taking cetirizine or levocetirizine. Some patients also found success with a tapering approach after restarting the medication, gradually reducing their dosage over time rather than stopping abruptly.
Healthcare professionals are now advised to discuss this potential risk with patients, particularly when prescribing or recommending these medications for chronic use. The Consumer Healthcare Products Association has expressed support for the FDA’s efforts to notify the public about this safety signal, even though the reaction appears to be relatively rare.
Recommendations for Patients
If you currently take cetirizine (Zyrtec) or levocetirizine (Xyzal) regularly, the FDA emphasizes that you should not stop taking these medications abruptly without consulting your healthcare provider. This is especially important if you’ve been using them continuously for months or years. Your doctor can provide personalized guidance on whether continued use is appropriate or how to safely discontinue if necessary.
Patients who experience severe itching after stopping either medication should contact their healthcare provider and consider reporting their experience to the FDA’s MedWatch program. While this withdrawal effect can be distressing, understanding the potential risk and working closely with healthcare providers can help manage the discontinuation process more effectively and minimize complications.