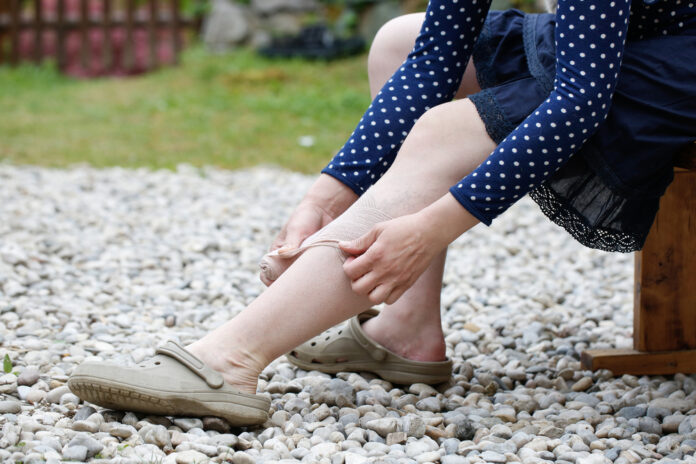
If a blood clot develops, usually in the legs but not always, it may result in deep vein thrombosis. Sometimes there are no overt symptoms. Everyone should be aware of DVT because it can cause serious illness, disabilities, and in very serious cases, death. There is good news, though, if detected early, DVT can be treated and prevented.
You need to keep an eye out for difficulties if you have specific medical conditions, including DVT, that affects how your blood clots. For instance, a blood clot in the legs could form if you sit stationary for a long time. Make sure you are up and moving around as much as you can, especially if you are on a long trip or recovering from surgery in bed. Below is a list of other risk factors.
Deep vein thrombosis can be risky because blood clots in the veins can separate. Once in the bloodstream, the clots may go to the lungs and lodge there, preventing blood flow and leading to pulmonary embolism. The combination of DVT and pulmonary embolism is referred to as venous thromboembolism.
Risk Factors of DVT
As mentioned, deep vein thrombosis can happen to almost anyone. But some things can make it more likely to exist. With one or more of these factors present simultaneously, the chance is increased much more.
The factors listed below raise the possibility of getting DVT:
- Fractures,
- Serious muscular damage
- A significant operation, particularly involving the abdomen, pelvis, hip, or legs
- Slow blood flow – commonly brought on by bed confinement or restricted movement
- Paralysis
- Elevated estrogen – frequently brought on by birth control, menopause, or hormone replacement
- Pregnancy, during and after for up to three months
- Certain chronic medical diseases, such as:
Heart condition
Lung condition
Ways to Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Consider using medical compression stockings
- Ask your physician about anticoagulants to stop DVT
- When spending time sitting down, get up and go for a stroll
- Put on comfortable clothing
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding a sedentary lifestyle
- Adhering to your doctor’s advice based on your particular risk factors
Possible Symptoms of DVT
Most DVT patients have no symptoms at all. The most typical signs of DVT in the area of the body afflicted are as follows:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Red skin
Talk with your physician about an appointment if you notice any of these symptoms.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16911-deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt-thrombophlebitis
https://www.healthline.com/health/deep-venous-thrombosis#symptoms