Shingles is a viral infection that gives you a painful, burning skin rash. Depending on your skin tone, this can appear as a red, dark pink, or dark brown mark. Read this article to learn more about the symptoms of this disease, its causes, risk factors, treatments, and prevention methods.
What Is Shingles?
Shingles is a disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is also responsible for chickenpox. Even after the chickenpox infection is over, the virus stays dormant in your system for years before becoming shingles.
Symptoms of Shingles
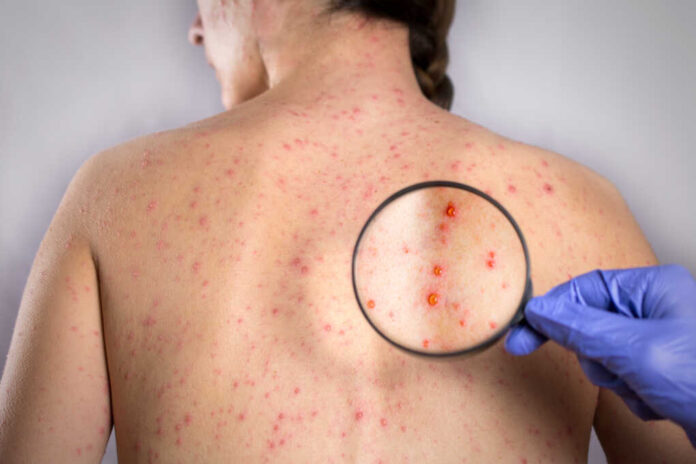
According to the CDC, the first symptoms of shingles are pain and burning. The pain usually happens on one side of your body and along a particular skin area called a dermatome. This is followed by a rash that can be red, dark pink, or dark brown, depending on your skin tone.
The National Institute on Aging (NIA) also characterizes shingles with the following symptoms:
● A rash on your face and ears
● Itchiness
● Burning sensation
● Fluid-filled blisters that break easily
Shingles On Your Face
Shingles can give you a rash on your face and lead to:
● Loss of hearing
● Weakness in your facial muscles
● Issues with your balance
Shingles On Your Eyes
In some cases, a blistering rash could appear on your eyes with the following symptoms:
● Swelling
● Blurred vision
● Redness and tearing
Shingles Causes
Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which also causes chickenpox. If you’ve already had chickenpox, you can suffer from shingles when the virus reactivates in your body.
You could also develop the disease if you have the following risk factors:
● A weak immune system
● Aging
● Emotional stress
Shingles Treatments
There is no cure for shingles, but treating it immediately can reduce your risk of complications and speed up your recovery. You can use the following medications to treat shingles:
● Antiviral medications like acyclovir and valacyclovir to reduce pain and boost recovery speed
● Anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen to ease pain and swelling.
● Antihistamines like diphenhydramine to treat itching
How To Prevent Shingles
According to the NIA, receiving vaccinations can stop you from developing severe shingles complications. All children should also receive two doses of the chickenpox vaccine, also called varicella immunization.
Adults aged 50 and older should get a shingles vaccine called varicella-zoster immunization.
Conclusion
Shingles is an infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is also responsible for chickenpox. Once it infects your system, it remains dormant before it reactivates as shingles.
You must visit your doctor if you suspect you have shingles, especially if you have a high development risk. You should also visit a dermatologist within 3 days to prevent long-term complications.