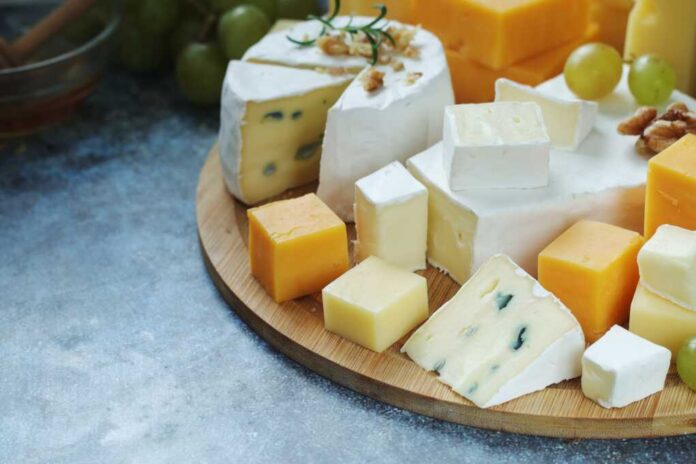
Dairy’s Role in Cardiovascular Health. Dairy products are challenging long-held beliefs, revealing unexpected benefits for heart health.
Story Snapshot
- New research challenges the idea that only low-fat dairy is heart-healthy.
- Studies suggest moderate consumption of dairy may reduce stroke and CVD risk.
- Cheese and yogurt show potential cardiovascular benefits.
- Dietary guidelines may need updates to reflect new findings.
- Conflicting evidence highlights the need for personalized dietary advice.
Reevaluation of Dairy’s Health Impact
Recent studies are prompting a reevaluation of traditional dietary guidelines that favor low-fat dairy for heart health. Emerging evidence suggests that moderate consumption of both low- and full-fat dairy products may offer cardiovascular benefits, contradicting previous assumptions. This shift is particularly relevant for conservatives who value personal choice and skepticism towards one-size-fits-all dietary recommendations.
The findings draw attention to specific dairy products, such as cheese and yogurt, which may contribute positively to heart health. These products have been associated with reduced risks of stroke and cardiovascular disease (CVD), challenging the notion that all saturated fats are detrimental. However, the need for further research is evident, as some studies still suggest caution with high-fat milk consumption.
Major meta-analysis just dropped analyzing 33 studies on dairy and health – turns out the dairy debate is way more nuanced than 'good vs bad'
The cardiovascular findings are pretty interesting:
➡️Total dairy shows weak protective effects against CVD
➡️Yogurt consistently… pic.twitter.com/Fg1X6cdQz5— TheHealthyRD (@HeidiHmoretti) September 11, 2025
Global and Product-Specific Perspectives
The insights into dairy’s cardiovascular effects emerge from large multinational studies like the PURE study, which examine diverse populations and dietary contexts. This comprehensive view highlights that dairy’s impact on heart health can vary based on the type of product and individual dietary patterns. It underscores the complexity of nutritional science and the importance of not oversimplifying dietary advice.
Despite the promising results, there remains a call for caution. Some researchers point out the potential risks associated with high consumption of certain dairy products, emphasizing the need for balanced and personalized dietary recommendations. The complexity of dairy’s effects requires ongoing investigation to better understand its role in heart health across different populations.
Implications for Dietary Guidelines and Public Perception
The evolving evidence has significant implications for dietary guidelines and public health messaging. If future research continues to support these findings, public health agencies might consider revising guidelines to reflect the potential benefits of moderate dairy consumption. Such updates could influence consumer behavior, agricultural markets, and broader societal views on dairy.
These findings reinforce the importance of individual decision-making in diet. The ongoing debate highlights the need for clear, evidence-based guidelines that accommodate diverse dietary preferences and health needs, respecting personal liberty and choice.
Sources:
Beyond Bone Strength: The Cardiovascular Benefits of Everyday Dairy Foods
Rethinking Dairy Fat and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from Expert Review
Dairy Nutrition: Evidence and Expert Review
Dairy and Cardiovascular Health: Current Perspectives