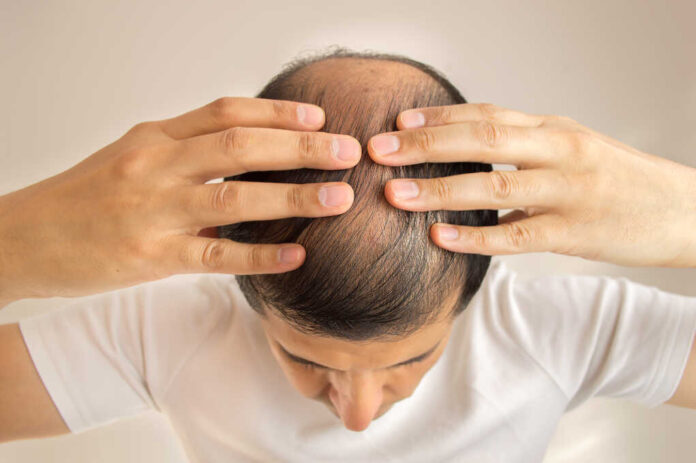
Scientists have discovered a biological “switch” that can wake up dormant hair follicles and potentially end baldness forever.
Story Highlights
- UCLA and Harvard researchers identified metabolic pathways that control hair follicle stem cell activation
- Two topical drugs successfully reactivated dormant hair follicles in mouse studies by targeting lactate metabolism
- The same neural mechanism that causes goosebumps also regulates long-term hair regeneration
- This approach bypasses traditional hormone-based treatments that have limited effectiveness and side effects
Revolutionary Discovery Targets Root Cause of Hair Loss
UCLA and Harvard researchers have cracked the code on hair regeneration by identifying the metabolic switch controlling hair follicle stem cells. Unlike previous treatments that focused on hormones, this breakthrough targets the cellular energy pathways that determine whether dormant hair follicles wake up or remain inactive. Dr. Heather Christofk and Dr. William Lowry at UCLA discovered that lactate metabolism serves as the critical activator, offering a completely new therapeutic approach.
This Breakthrough Drug Wakes Up Sleepy Hair Follicles. It May Be the Ultimate Baldness Cure, Scientists Say.
A hidden biological switch controls hair growth. Scientists just learned how to flip it back on and kickstart the process.
https://t.co/vaQUJhmQLU— timethief Canadian forever🍁🦫 🇨🇦 (@timethief) September 3, 2025
Metabolic Pathway Holds Key to Hair Regeneration
The research reveals that hair follicle stem cells require specific metabolic conditions to shift from dormancy to active hair production. Scientists found that lactate dehydrogenase activity and glycolysis pathways must be activated for stem cells to regenerate hair. This metabolic switch operates independently of the hormonal factors targeted by current treatments like minoxidil and finasteride, explaining why existing solutions often fail to deliver consistent results.
Goosebumps Connection Reveals Neural Control System
Harvard researchers made the surprising discovery that sympathetic nerve-muscle interactions responsible for goosebumps also control hair follicle regeneration. This neural regulation system connects environmental stimuli like cold exposure to long-term hair growth cycles. The finding demonstrates that hair regeneration involves complex interactions between metabolic, neural, and stem cell systems, providing multiple potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Clinical Translation Shows Promising Results
Preclinical studies using topical drug applications successfully activated dormant hair follicle stem cells in mouse models. The two identified compounds work by modulating lactate metabolism pathways, triggering stem cell activation without the side effects associated with hormonal treatments. While human trials are still needed, the targeted approach addresses fundamental biological mechanisms rather than symptoms, suggesting more effective and lasting results than current options.
This breakthrough represents a paradigm shift from treating hair loss as a hormonal problem to addressing it as a stem cell activation challenge. The research opens new possibilities for individuals suffering from various forms of alopecia, including chemotherapy-induced hair loss, offering hope where traditional treatments have failed to deliver satisfactory outcomes.
Sources:
UCLA scientists identify new way to activate stem cells to make hair grow
Lactate dehydrogenase activity and HFSC activation research
Molecular mechanisms of stem cell dynamics in hair follicles
IL-1 signaling and HFSC proliferation study
Goosebumps and hair follicle stem cell regulation